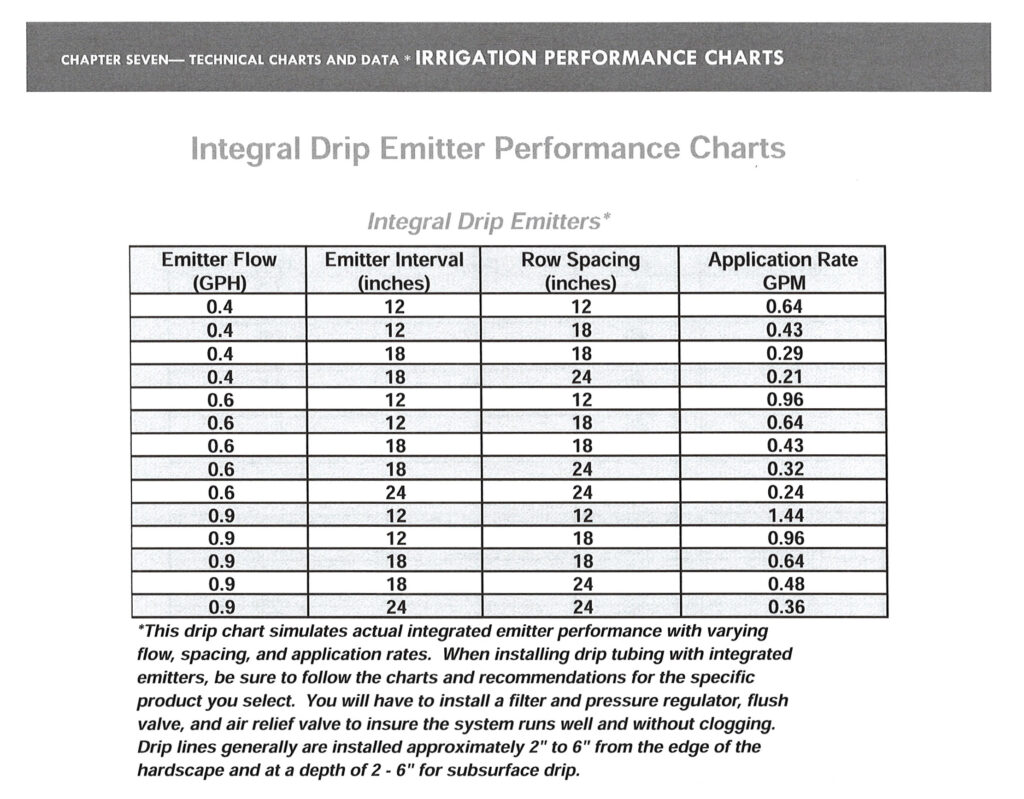
Drip Line Performance Chart – Lawn Sense
Use this chart to calculate your actual GPM (Gallons Per Minute) that your drip line is using. You’ll need to know the specs on the drip line hose that was installed, as well as the valve controlling that zone.
You can also get your GPH (Gallons Per Hour) manually by running the drip zone for one hour and checking the water meter before and after to see how many gallons you’ve used.