 Rotor Head Performance Charts
Rotor Head Performance Charts
Rotor heads are a vital component of many irrigation systems, offering adjustable and precise water delivery for large areas. These Rotor Head Performance Charts provide essential information for selecting and configuring rotor heads to ensure an efficient and evenly distributed water application. Properly understanding these charts can help maintain a healthy landscape while minimizing water waste.
How to Use the Rotor Head Performance Chart
- Identify the Rotor Head Type:
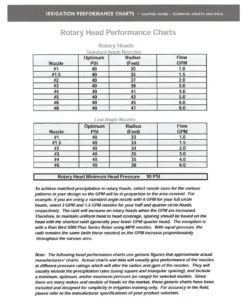
The chart categorizes rotor heads into Standard Angle Nozzles and Low Angle Nozzles, each suited for specific irrigation needs. Standard angle nozzles provide a broader radius, while low-angle nozzles are ideal for areas prone to wind drift or requiring closer water delivery. - Determine the Nozzle Size:
Select a nozzle size based on the radius and flow requirements for your irrigation zone. For example:- A #4 Standard Angle Nozzle at 40 PSI offers a 41-foot radius with a flow rate of 4.0 GPM.
- A #4 Low Angle Nozzle at 40 PSI provides a 35-foot radius with a flow rate of 4.0 GPM.
- Check Minimum Operating Pressure:
The chart specifies a Rotary Head Minimum Head Pressure of 30 PSI to ensure optimal performance. Always verify that your system maintains this minimum pressure. - Match Precipitation Rates:
Unlike spray heads, rotor heads require manual adjustment to achieve a matched precipitation rate (PR). For example:- A 360° rotor head with a 6.0 GPM nozzle will match precipitation if paired with a 3.0 GPM nozzle for 180° heads and a 1.5 GPM nozzle for 90° heads.
- Use the provided nozzle tree to select the appropriate nozzle sizes.
- Calculate Total GPM:
Multiply the GPM of each rotor head by the total number of heads in the zone. This helps determine the flow capacity required for your irrigation system. - Account for Spacing:
The spacing between heads should overlap slightly to maintain uniform coverage. Use the radius measurements in the chart to guide placement.
FAQs About Rotor Head Performance Charts
1. What is matched precipitation, and why is it necessary?
Matched precipitation ensures that water is evenly distributed across all areas of your irrigation zone, regardless of the arc of each rotor head. It prevents overwatering or underwatering specific sections of the landscape.
2. How do I know which nozzle size to use?
Choose a nozzle size based on the radius needed for the area being watered and the flow capacity (GPM) of your irrigation system. Refer to the chart for precise flow rates at specific pressures.
3. What is the difference between Standard Angle and Low Angle Nozzles?
- Standard Angle Nozzles: Provide a higher trajectory and broader coverage, ideal for open areas with minimal wind interference.
- Low Angle Nozzles: Deliver water at a lower trajectory, reducing wind drift and improving efficiency in windy or constrained spaces.
4. How do I adjust rotor heads for a matched precipitation rate?
Use the nozzle tree provided with the rotor head to install the correct nozzle size for each arc:
- Full-circle (360°) heads require the highest GPM nozzle.
- Half-circle (180°) heads use a nozzle with half the GPM of the full-circle head.
- Quarter-circle (90°) heads use a nozzle with one-quarter the GPM of the full-circle head.
5. Can rotor heads be used on slopes?
Yes, but additional considerations like check valves and pressure regulation may be necessary to prevent runoff or pooling at the base of the slope.
6. How often should I inspect my rotor heads?
Inspect rotor heads monthly during the irrigation season to ensure nozzles are free of debris, arcs are properly adjusted, and precipitation rates are matched.
7. Why is the minimum operating pressure important?
Operating below the specified minimum pressure (30 PSI) can lead to incomplete coverage and inefficient water distribution.
Tips for Optimizing Rotor Head Performance
- Perform Routine Maintenance: Clean and inspect rotor heads regularly to ensure optimal performance and prevent clogs.
- Use Manufacturer-Specific Nozzles: Mixing nozzles from different brands can lead to mismatched precipitation rates.
- Install Pressure Regulators: Consistent pressure ensures uniform water distribution and prevents over-spraying.
- Account for Wind Conditions: Use low-angle nozzles in windy areas to minimize water drift and improve accuracy.
- Calculate Precipitation Rate (PR): Use the formula: PR = (96.3 × Total GPM ) / Irrigated Area in Square Feet
- This ensures your irrigation schedule aligns with the landscape’s water requirements.
By understanding and applying the information in the Rotor Head Performance Charts, you can achieve a highly efficient irrigation system tailored to your landscape’s specific needs. Proper nozzle selection, matched precipitation rates, and routine maintenance will ensure healthy, lush greenery while conserving water resources.